Types of Business Inventory Apps
App for business inventory – Choosing the right inventory management app is crucial for efficient business operations. The market offers a variety of solutions, each catering to different needs and business sizes. Understanding the key distinctions between these app types is essential for making an informed decision.
App Categories and Their Features
Inventory management apps fall into several categories, each with its own set of features and target audience. Key differences lie in deployment (cloud-based vs. on-premise), specialization (general purpose vs. industry-specific), and scalability.
| App Type | Features | Target Business Size | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-based Inventory App | Real-time tracking, multi-user access, data backups, mobile accessibility, automated reporting, integrations with other systems. | Small, Medium, Large | Subscription-based (monthly or annual fees) |
| On-premise Inventory App | Similar features to cloud-based, but requires dedicated server and IT infrastructure. Offers greater control over data security but lacks accessibility from remote locations. | Medium, Large | One-time purchase or perpetual license |
| Specialized Industry Solution | Tailored features specific to a particular industry (e.g., retail, manufacturing, healthcare). May offer specialized reporting and compliance features. | Small, Medium, Large | Subscription-based or one-time purchase, often with tiered pricing based on features and user count. |
| Small Business Inventory App | Simplified interface, basic inventory tracking, limited reporting features. Often cloud-based and affordable. | Small | Subscription-based, typically with lower monthly fees. |
| Enterprise Inventory Management System (IMS) | Comprehensive features, advanced analytics, robust integrations, scalability for large volumes of data and users. | Large | High subscription fees, often based on user count and data volume. |
Key Features of Business Inventory Apps: App For Business Inventory
Effective inventory management relies on several core functionalities offered by modern apps. These features streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency.
Real-time Inventory Tracking
Real-time tracking provides an up-to-the-minute view of inventory levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions regarding purchasing, production, and sales. This eliminates stockouts and reduces the risk of overstocking.
Barcode and RFID Integration
Source: ctfassets.net
Integrating barcode and RFID technology significantly speeds up inventory processes. Barcodes allow for quick and accurate scanning of individual items, while RFID tags enable tracking of multiple items simultaneously, improving accuracy and efficiency, especially for large volumes of inventory.
Supply Chain Efficiency Improvements
Inventory management apps enhance supply chain efficiency by optimizing stock levels, improving order fulfillment, and reducing lead times. Real-time data allows businesses to anticipate demand, proactively manage inventory, and collaborate more effectively with suppliers.
Inventory Management Process Flowchart
A typical inventory management process using an app would involve the following steps:
- Receiving Inventory: Scan barcodes/RFID tags upon arrival, update inventory levels in the app.
- Storage and Organization: Assign locations to items within the warehouse and update the app accordingly.
- Order Fulfillment: Use the app to track orders, locate items, and manage picking and packing.
- Shipping and Delivery: Update the app with shipping information and track delivery status.
- Inventory Adjustments: Regularly reconcile physical inventory with app data, addressing discrepancies.
- Reporting and Analysis: Generate reports on inventory levels, sales trends, and other key metrics.
Integration with Other Business Systems
Seamless integration with existing business systems is crucial for maximizing the benefits of an inventory management app. This integration streamlines data flow and eliminates manual data entry.
Integration with Accounting Software
Integrating an inventory app with accounting software automates the recording of inventory transactions, reducing errors and saving time. This ensures accurate financial reporting and simplifies the reconciliation process.
Integration with Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems
Integrating with POS systems provides real-time updates on inventory levels based on sales data. This prevents stockouts and ensures accurate inventory tracking at the point of sale.
Challenges in System Integration
Challenges can arise from compatibility issues between different systems, data format differences, and the need for custom integrations. Careful planning and selection of compatible apps are essential to minimize these challenges.
Potential Integration Points
- Accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero)
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems (e.g., Square, Shopify)
- Customer relationship management (CRM) systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot)
- E-commerce platforms (e.g., Amazon, eBay)
- Shipping and logistics providers (e.g., FedEx, UPS)
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Implementing an inventory management app involves costs, but the potential ROI can be substantial. Understanding both the costs and the benefits is crucial for making a sound investment decision.
Pricing Models
Inventory apps typically use subscription-based pricing (monthly or annual fees) or one-time purchase models. Subscription models often include automatic updates and ongoing support, while one-time purchases require separate maintenance contracts.
Calculating ROI
ROI can be calculated by subtracting the total costs (implementation, subscription fees, training) from the total benefits (reduced waste, improved efficiency, increased sales) and dividing the result by the total costs. For example, if a company invests $10,000 in an inventory app and realizes $20,000 in cost savings, the ROI is 100%.
Cost Minimization Strategies
Costs can be minimized by choosing a cloud-based solution (avoiding server infrastructure costs), opting for a smaller-scale app if appropriate for business needs, and leveraging free trials or demos to evaluate different options before committing.
Cost Factors and ROI Benefits
| Cost Factor | Description | ROI Benefit | Quantification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software License/Subscription | Recurring or one-time fees for the inventory app. | Reduced labor costs, minimized waste | Calculate the cost savings from reduced labor hours and waste reduction. |
| Implementation Costs | Costs associated with setup, data migration, and training. | Improved accuracy and efficiency | Measure the improvement in order fulfillment speed and accuracy. |
| Maintenance and Support | Ongoing costs for technical support, updates, and maintenance. | Increased sales and profitability | Track sales growth and profit margins after implementing the app. |
Security and Data Management
Data security is paramount in inventory management. Protecting sensitive inventory data from unauthorized access and loss is crucial for maintaining business continuity and complying with regulations.
Data Security Measures
Inventory apps employ various security measures, including encryption (to protect data in transit and at rest), access controls (to limit access to authorized personnel), and regular security audits.
Data Backup and Recovery
Regular data backups are essential for business continuity in case of data loss or system failure. Cloud-based apps often offer automated backup and recovery features. For on-premise solutions, a robust backup strategy is crucial.
Security Considerations
- Data encryption (both in transit and at rest)
- Access controls and user authentication
- Regular security updates and patches
- Data backup and recovery plan
- Compliance with relevant data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)
User Experience and Interface Design
A user-friendly interface is critical for efficient inventory management. A well-designed app simplifies tasks, reduces errors, and encourages adoption by employees.
Ideal User Interface
The ideal interface should be intuitive, easy to navigate, and visually appealing. Key features should be easily accessible, and data should be presented in a clear and concise manner. Customizable dashboards and reports allow users to tailor the app to their specific needs.
User-Friendly Features
Examples of user-friendly features include intuitive dashboards displaying key metrics, customizable reports, drag-and-drop functionality for inventory management, and mobile accessibility for on-the-go updates.
Importance of Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility allows for real-time inventory updates from anywhere, enabling quicker responses to changing inventory levels and improved efficiency in warehouse operations.
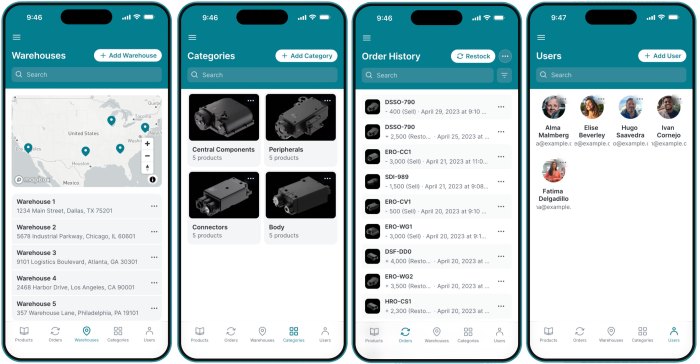
User-Friendly Dashboard Mock-up

Source: apkcombo.org
A sample dashboard might include: A summary of total inventory value, a visual representation of stock levels (e.g., bar chart), a list of low-stock items, a quick-access menu for common tasks (e.g., adding new items, generating reports), and a notification system for critical events (e.g., low stock alerts).
Selecting the Right App for Your Business
Choosing the right inventory management app requires careful consideration of several factors. A structured approach to evaluation will help businesses identify the best fit for their specific needs.
Factors to Consider
Key factors include business size, industry, budget, existing IT infrastructure, and the specific features required. A thorough needs assessment is essential before beginning the selection process.
Efficient inventory management is crucial for any business, and thankfully, numerous apps cater to this need. Understanding your leadership style is equally important, and taking a test like the 7-eleven business leadership inventory test can offer valuable insights. This self-awareness can then be applied to optimize your inventory app usage and overall business strategy, ensuring smooth operations and improved profitability.
Ultimately, the right app combined with effective leadership makes a significant difference.
Decision-Making Framework
A decision matrix can be used to compare different app options based on predefined criteria. Each criterion is weighted according to its importance, and each app is scored based on its performance in each area.
Questions to Ask Vendors
Before selecting an app, it is essential to ask potential vendors about their pricing models, security measures, integration capabilities, customer support, and training options.
Selection Criteria, App for business inventory
| Selection Criteria | Importance | Evaluation Method | Example Questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | High | Compare pricing models and total cost of ownership. | What are the licensing fees? What are the ongoing maintenance costs? |
| Features | High | Evaluate features against business needs. | Does the app offer real-time tracking? What reporting capabilities are available? |
| Integrations | Medium | Assess compatibility with existing systems. | Does the app integrate with our accounting software? Can it integrate with our POS system? |
| Security | High | Review security measures and data protection policies. | What security measures are in place to protect our data? What is your data backup and recovery plan? |
FAQs
What is the average cost of a business inventory app?
Costs vary widely depending on features, scalability, and vendor. Expect to find options ranging from free (often with limited functionality) to several hundred dollars per month for enterprise-level solutions.
How do I ensure my inventory data is secure?
Look for apps with robust security measures like encryption, access controls, and regular data backups. Read reviews and check vendor certifications to ensure data protection is a priority.
Can I integrate my inventory app with existing software?
Many apps offer integration with popular accounting and POS systems. Check the app’s specifications or contact the vendor to confirm compatibility with your existing software.
What kind of training is required to use a business inventory app?
Training needs vary. Some apps are very user-friendly and require minimal training, while others may need more extensive onboarding depending on their complexity and features.